Research Projects
Video VPR
The Video Visual Place Recognition project aims to create a robust and efficient system that can recognize and match specific places in videos. By extracting distinctive visual features, representing them, and employing matching algorithms, the system can identify locations across different videos. It also focuses on localization, mapping, and handling challenges like changes in lighting and occlusions. The project's applications include autonomous navigation, augmented reality, and video surveillance. The goals include developing an accurate system, optimizing processing speed, evaluating performance, and exploring incremental learning techniques. Overall, this project aims to advance computer vision technology and its practical applications in diverse domains.
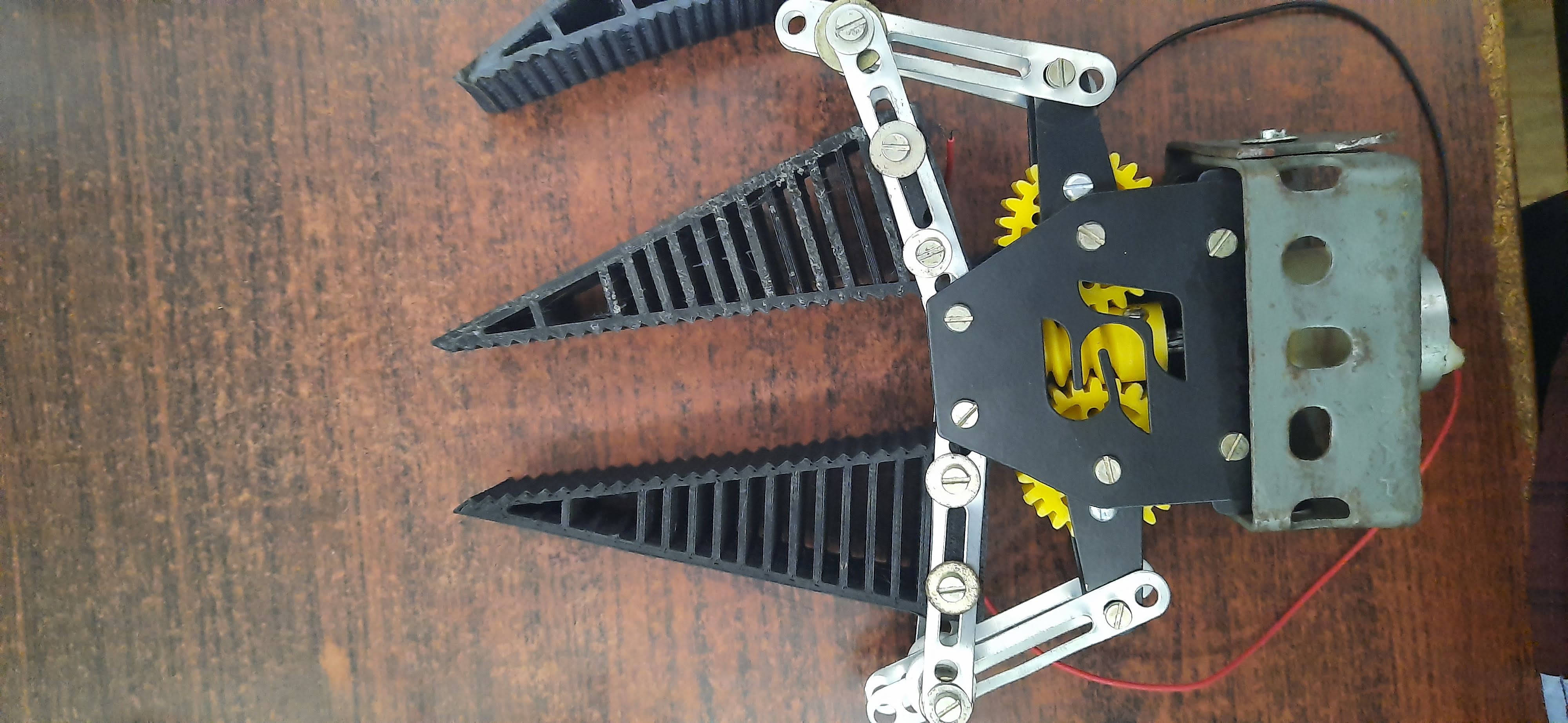
Flexible gripper
 This project focuses on the development of a bio-inspired two-fingered gripper with a Fin Ray (fish fin) structure and grooves on the contact side. The gripper is composed of soft cross beams that were optimized using the finite element method. Three different geometries were considered: Even, Uneven, and Semi-filled configurations. The grippers were 3D printed using Polyurethane material. The gripper with uneven cross beams showed controlled displacement and had the ability to handle various geometries and materials within its gripper length and payload capacity. The project aims to enhance the compliance and dexterity of robotic manipulators, making them safer for interaction with humans. The gripper design was inspired by fish fins and the Fin Ray Effect was utilized to improve grasping ability. The experiment involved simulation analysis using Inventor 2021 and physical testing using an articulated robot. The results demonstrated the effectiveness of the gripper in gripping different objects.
This project focuses on the development of a bio-inspired two-fingered gripper with a Fin Ray (fish fin) structure and grooves on the contact side. The gripper is composed of soft cross beams that were optimized using the finite element method. Three different geometries were considered: Even, Uneven, and Semi-filled configurations. The grippers were 3D printed using Polyurethane material. The gripper with uneven cross beams showed controlled displacement and had the ability to handle various geometries and materials within its gripper length and payload capacity. The project aims to enhance the compliance and dexterity of robotic manipulators, making them safer for interaction with humans. The gripper design was inspired by fish fins and the Fin Ray Effect was utilized to improve grasping ability. The experiment involved simulation analysis using Inventor 2021 and physical testing using an articulated robot. The results demonstrated the effectiveness of the gripper in gripping different objects.
Graduate Projects
Brick Laying Robot
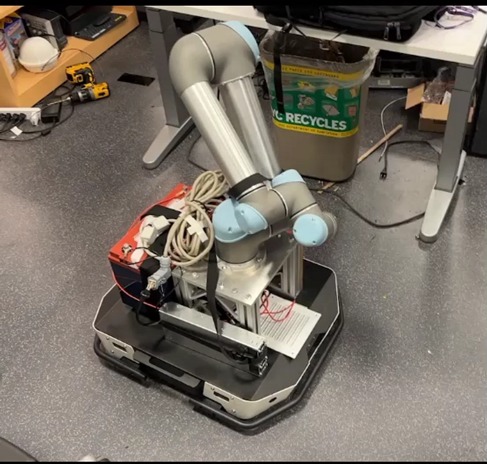 Designed and implemented a robotic system integrating UR5 manipulator and AgileX Tracer for automated construction tasks.
Designed and implemented a robotic system integrating UR5 manipulator and AgileX Tracer for automated construction tasks.
- Developed algorithms for seamless and synchronized control of both robots.
- Enabled precise bricklaying capabilities.
- Utilized a 24-volt DC power system for efficient operation.
Skills: Robotics integration, motion control, algorithm development, automation

DoorDash Delivery Robot
 Developed a versatile robotic delivery system by: Integrating a Husky mobile robot with a Xarm manipulator arm.
Developed a versatile robotic delivery system by: Integrating a Husky mobile robot with a Xarm manipulator arm.
- Successfully combined the mobility platform of Husky with the manipulation capabilities of Xarm for a comprehensive solution.
- Enabled functionalities for:
- Automated door opening
- Package delivery
- Object manipulation across different rooms
Skills: Robot integration, path planning, object manipulation, automation
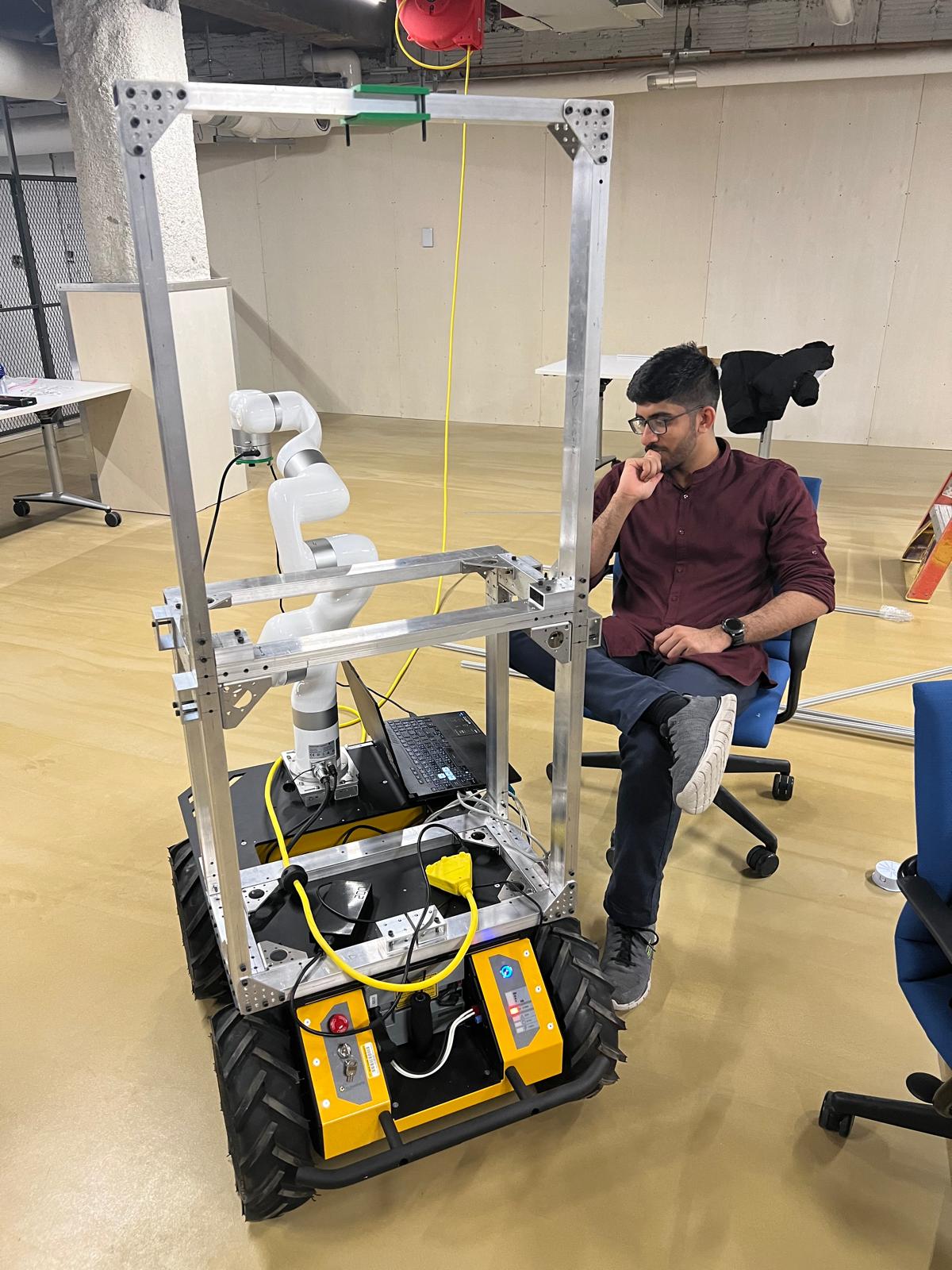
Mobile Object Rearrangement
 Developed a camera-guided robot for autonomous 2D structure building through mobile manipulation. Tackled adaptability, collision avoidance, and precise object placement. Implemented navigation & manipulation algorithms, explored reinforcement learning for adaptation, built a simulation environment, and achieved successful real-world testing. This experience highlights:
Developed a camera-guided robot for autonomous 2D structure building through mobile manipulation. Tackled adaptability, collision avoidance, and precise object placement. Implemented navigation & manipulation algorithms, explored reinforcement learning for adaptation, built a simulation environment, and achieved successful real-world testing. This experience highlights:
- My ability to design and develop robotic systems
- Expertise in robot navigation and manipulation algorithms
- Proficiency in simulation and real-world testing
Skills: Pose Net Neural Network, Object manipulation, Real World data collection
Build Manipulation
 In this project, I Led the development of a camera-guided robot for autonomous 2D structure building. Tackled challenges like adaptability, collision avoidance, and precision. Built a simulation environment, implemented navigation/manipulation algorithms, and achieved successful real-world testing. Highlights include:
In this project, I Led the development of a camera-guided robot for autonomous 2D structure building. Tackled challenges like adaptability, collision avoidance, and precision. Built a simulation environment, implemented navigation/manipulation algorithms, and achieved successful real-world testing. Highlights include:
- Reinforcement learning for autonomous navigation and structure construction
- Algorithmic solutions for adaptability & collision avoidance
- Environment modifications to enhance object pushing efficiency
- Validation through simulation & real-world testing
Skills: Reinforcement Learning(PPO Clip), A* Path Planning, Object manipulation, PoseNet Neural Network
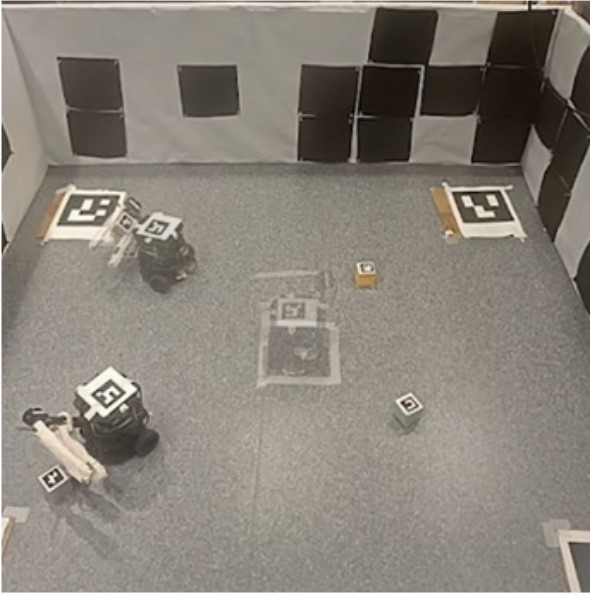
Maze Mapping and Navigation
 In this project, maze mapping and navigation is acheived developing a sophisticated algorithm tailored to tackle the challenges of maze-like indoor environments. some of the algorithms that were used halped to map the maze and effectively navigate through the setting autonomously with little to no human inteference.
In this project, maze mapping and navigation is acheived developing a sophisticated algorithm tailored to tackle the challenges of maze-like indoor environments. some of the algorithms that were used halped to map the maze and effectively navigate through the setting autonomously with little to no human inteference.
- Utilization of advanced computer vision techniques like SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform) and SuperGlue, accurately identify target locations amidst complex maze layouts and parallely used for mapping the maze setting.
- Leveraed the A* path planning algorithm to autonomlusly plan paths from start locations to identifeid target location (global planner)
- Vanishing points mehod was used to effectevielt present he robot from colliding with the walls (local planner)
Skills: A* Path Planning, Localisation and Navigation, SIFT/SURF, Vanishing points, Camera collibration
Tracking using YOLO-v7
![]() This project uses YOLOv7, a fast and accurate real-time object detection algorithm, to track cars on a highway.
The repository includes images (potentially used for training/testing) and videos demonstrating the tracking results.
You can explore the code to understand how YOLOv7 is implemented for this specific task.
YOLOv7 excels in real-time applications due to its single forward pass processing and achieves high accuracy and speed in object detection. This project showcases its versatility for object tracking.
This project uses YOLOv7, a fast and accurate real-time object detection algorithm, to track cars on a highway.
The repository includes images (potentially used for training/testing) and videos demonstrating the tracking results.
You can explore the code to understand how YOLOv7 is implemented for this specific task.
YOLOv7 excels in real-time applications due to its single forward pass processing and achieves high accuracy and speed in object detection. This project showcases its versatility for object tracking.
Skills: Machine Learning
Miniature AGV for material handling
 The Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) is a revolutionary solution for material handling and transportation. It was inspired by the industrial forklift and designed to move pallets from one location to another using just a few inputs from the user. The AGV offers many benefits over traditional manual labor, including increased efficiency, reduced risk of accidents and damage, and reduced costs.
The Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) is a revolutionary solution for material handling and transportation. It was inspired by the industrial forklift and designed to move pallets from one location to another using just a few inputs from the user. The AGV offers many benefits over traditional manual labor, including increased efficiency, reduced risk of accidents and damage, and reduced costs.
Some of the key features of our scaled automated AGV are
- Minimal user input
- Intuitive GUI
- Navigation using the onboard encoder and IMU sensors
- Efficient and safe movement of pallets
- Compact size and mobility
Skills: Teamwork · Kalman filtering · Simulations
WidgetMover AGV
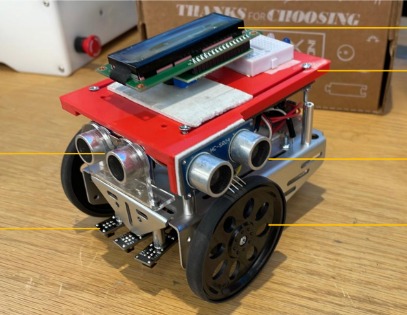 WidgetMover is an autonomous guided vehicle designed for efficient factory operations. It navigates a layout with three lanes, discovers widgets in lane A, and moves them to specific locations in lane B. Utilizing the A* algorithm, WidgetMover dynamically generates optimal paths, adapting to obstacles encountered using ultrasonic sensors. Equipped with QTI infrared sensors for line following and Parallax Continuous Servo actuators, the robot efficiently maneuvers through intersections while obeying lane constraints. By streamlining widget transportation and adaptive navigation, WidgetMover optimizes factory operations and enhances productivity.
WidgetMover is an autonomous guided vehicle designed for efficient factory operations. It navigates a layout with three lanes, discovers widgets in lane A, and moves them to specific locations in lane B. Utilizing the A* algorithm, WidgetMover dynamically generates optimal paths, adapting to obstacles encountered using ultrasonic sensors. Equipped with QTI infrared sensors for line following and Parallax Continuous Servo actuators, the robot efficiently maneuvers through intersections while obeying lane constraints. By streamlining widget transportation and adaptive navigation, WidgetMover optimizes factory operations and enhances productivity.
Some of the key features of our WidgetMover are
- Provide Pick and Place position
- Uses Button to collect input and displays the status appropriately
- Navigation using the IR sensors and ultrasonic sensors
- Uses A* for navigating from one point to another making it adaptable to any situation
Skills: Teamwork · A* · Propellor Board
AutoInventoryBot
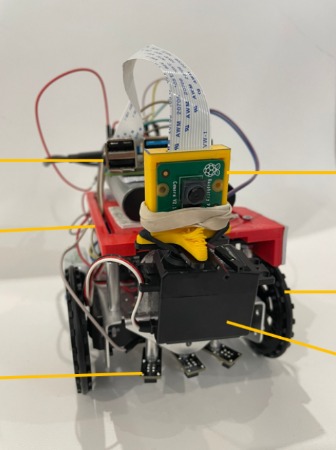 The AutoInventoryBot is an autonomous robot designed for warehouse inventory monitoring and management. The project aims to improve the efficiency and accuracy of inventory control by using robotics technology. The robot is equipped with hardware components such as QTI sensors for line-following, servo motors for motion control, a Parallax Propeller microprocessor for managing actions, a Raspberry Pi for processing camera data, a Pi camera for visual servoing, and a power distribution board for connecting the components. The robot uses ArUco tags to identify and count defective and non-defective widgets in the warehouse. It navigates the warehouse floor based on directional markers and counts the widgets at each station. The robot's goal is to reach its final destination and display the inventory count. The project aims to demonstrate how robotics can streamline inventory management processes and reduce the need for manual labor in warehouses.
The AutoInventoryBot is an autonomous robot designed for warehouse inventory monitoring and management. The project aims to improve the efficiency and accuracy of inventory control by using robotics technology. The robot is equipped with hardware components such as QTI sensors for line-following, servo motors for motion control, a Parallax Propeller microprocessor for managing actions, a Raspberry Pi for processing camera data, a Pi camera for visual servoing, and a power distribution board for connecting the components. The robot uses ArUco tags to identify and count defective and non-defective widgets in the warehouse. It navigates the warehouse floor based on directional markers and counts the widgets at each station. The robot's goal is to reach its final destination and display the inventory count. The project aims to demonstrate how robotics can streamline inventory management processes and reduce the need for manual labor in warehouses.
Some of the key features of our scaled automated AGV are
- Minimal user input
- Visual Servoing
- Navigation using QTI Sensor and A*
- Compact size and mobility
Skills: Teamwork · Kalman filtering · Simulations
AutoParkBot
 The project aims to develop an autonomous robot that can identify vacant parking spaces in a parking lot and navigate along a predetermined path. The robot utilizes sensors to detect lines on the ground and ultrasonic sensors to determine the presence of a vehicle in a parking space. The information is stored in the Arduino Uno microcontroller's memory and displayed using LEDs. The project utilizes QTI sensors for line following, ultrasonic sensors for obstacle detection, servo motors for controlling the robot's movement, and an Arduino Uno microcontroller as the brain of the system. The report discusses the motivation behind the project, its objectives, the hardware components used, and the potential future scope of the project.
The project aims to develop an autonomous robot that can identify vacant parking spaces in a parking lot and navigate along a predetermined path. The robot utilizes sensors to detect lines on the ground and ultrasonic sensors to determine the presence of a vehicle in a parking space. The information is stored in the Arduino Uno microcontroller's memory and displayed using LEDs. The project utilizes QTI sensors for line following, ultrasonic sensors for obstacle detection, servo motors for controlling the robot's movement, and an Arduino Uno microcontroller as the brain of the system. The report discusses the motivation behind the project, its objectives, the hardware components used, and the potential future scope of the project.
Some of the key features of our WidgetMover are
- The process is completely Autonomous with little-no human intervention
- Uses Button to collect input and displays the status appropriately
- Appropriate binary displays for indicating the numbers of cars and bikes
Skills: Teamwork · Line Following · Arduino Board · Binary Display
Undergraduate Projects
Autonomous Package Drone Delivery
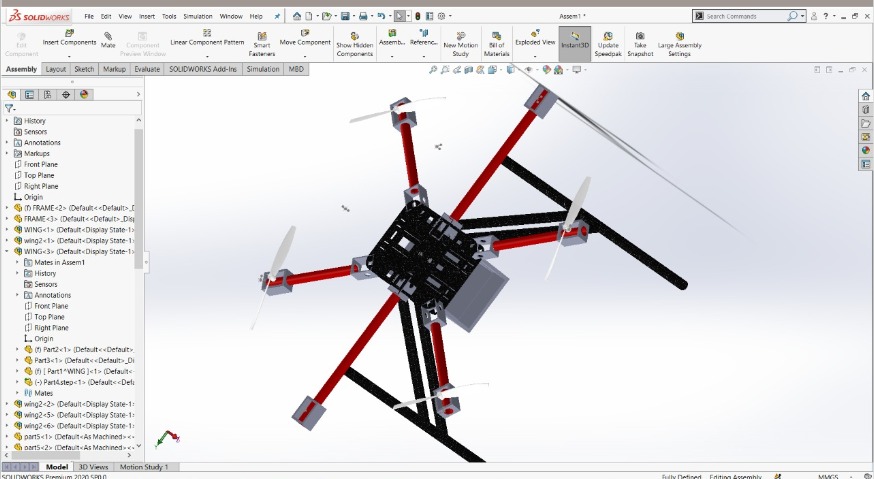 The use of autonomous drones for package delivery within a college campus is an innovative and cutting-edge solution that offers many advantages over traditional methods. The autonomous drone is designed to deliver packages from one point to another within the college campus, all while avoiding obstacles and ensuring safe and efficient delivery.
The use of autonomous drones for package delivery within a college campus is an innovative and cutting-edge solution that offers many advantages over traditional methods. The autonomous drone is designed to deliver packages from one point to another within the college campus, all while avoiding obstacles and ensuring safe and efficient delivery.
Some of the notable features of the bot are:
- Obstacle avoidance capability using stereo-cameras for depth perception and a ToF sensor for altitude determination.
- GPS for robot localization and path planning using the A* algorithm.
- Efficient and reliable delivery with no need for manual control or intervention.
- Compact size and mobility for flexible and versatile deployment.
- Improves efficiency and productivity by reducing the risk of accidents and damage.
- Reliable and cost-effective solution for package delivery within the college campus.
- Custom app for notifying the user of the status.
- Battery level indicator to calculate the flight path accordingly
Skills: Teamwork · Control Systems · Kalman filtering · Sensor Fusion · SLAM · Path Planning · Simulation
3 UPS 1 UPU Parallel Manipulator
 Parallel manipulators are becoming increasingly popular in various industries due to their unique design, high precision, and ability to manipulate objects in tight spaces. The 3-UPS 1-UPU parallel manipulator, also known as a 5-link manipulator, is a type of parallel manipulator that offers several advantages over other types of manipulators.
Parallel manipulators are becoming increasingly popular in various industries due to their unique design, high precision, and ability to manipulate objects in tight spaces. The 3-UPS 1-UPU parallel manipulator, also known as a 5-link manipulator, is a type of parallel manipulator that offers several advantages over other types of manipulators.
The features and benefits of the 3-UPS 1-UPU parallel manipulator are as follows:
- High precision and accuracy in object manipulation.
- Ability to manipulate objects in tight spaces.
- Real-time feedback allows for accurate and precise control.
- Electric prismatic actuation provides precise control over the movement.
- Flexible movement allows for easy navigation in tight spaces.
- Ideal solution for industrial and commercial applications requiring precision and maneuverability in tight spaces.
- Composed of 5 links connected by active and passive joints for flexible movement.
- Real-time feedback provided by sensors on the position and orientation of the manipulator's end-effector.
Unique design allows for use in tight spaces like borewells, manholes, and septic tanks
E-Transmission
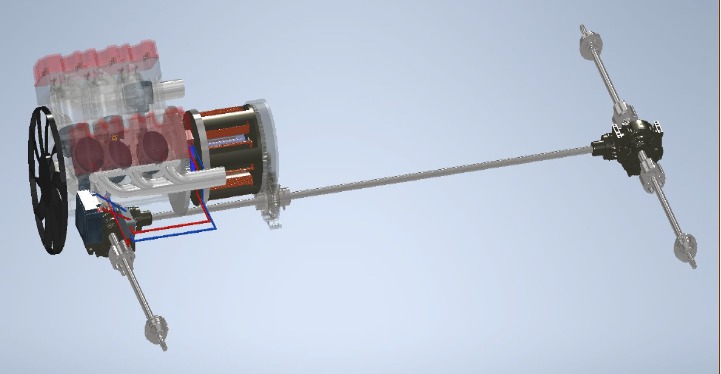 E-transmission is a cutting-edge technology that revolutionizes the way vehicles are powered and transmitted. It provides numerous benefits to drivers and vehicle owners alike, making the driving experience smoother, more efficient, and more reliable.
E-transmission is a cutting-edge technology that revolutionizes the way vehicles are powered and transmitted. It provides numerous benefits to drivers and vehicle owners alike, making the driving experience smoother, more efficient, and more reliable.
Some of the key features of E-transmission include:
- Advanced non-contact electromagnetic transmission
- Independent engine speed control, allowing for smooth power delivery even under varying road conditions and speeds
- Occupies less space than conventional transmission systems
- Increases the life of the vehicle by eliminating gears and clutches
- Improves the efficiency and reliability of power transmission from the engine to the road
- Reduces fatigue loading on the engine, resulting in longer engine life
- Combines the efficiency and range of an electric vehicle with the reliability of a traditional engine car
E-transmission provides a new and innovative solution for modern vehicles, offering a range of benefits over traditional transmission systems. Whether it be improved driving experience, increased efficiency, or longer vehicle life, the benefits of E-transmission are clear, and it is likely to play an important role in the future of the automotive industry.

Intelligent Line Marking Bot
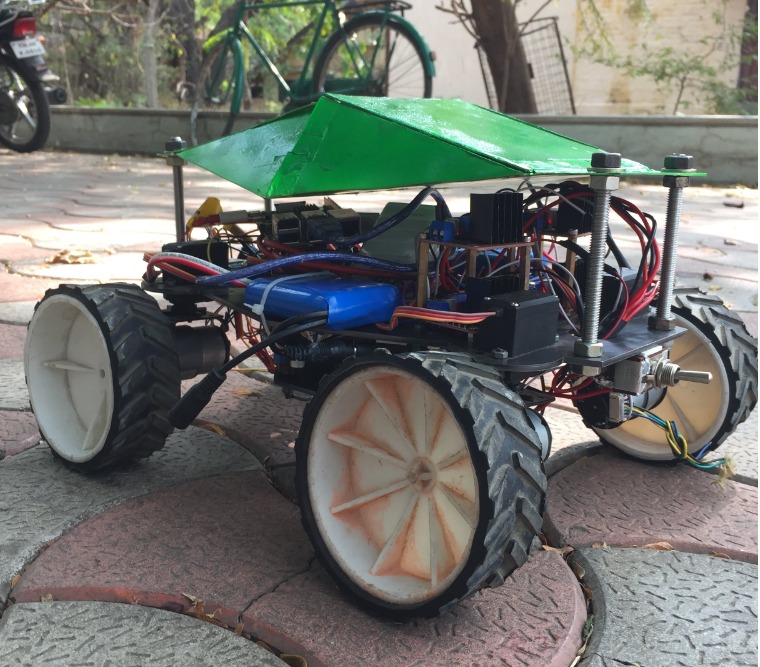 The Intelligent Line Marking Bot, a type of Automated Guidance Vehicle (AGV), is a robot designed to efficiently mark field lines on any sports field. The AGV is equipped with a range of onboard sensors, including GPS, IMU, and encoder, which work together to provide reliable data that is used for path planning and localization.
The Intelligent Line Marking Bot, a type of Automated Guidance Vehicle (AGV), is a robot designed to efficiently mark field lines on any sports field. The AGV is equipped with a range of onboard sensors, including GPS, IMU, and encoder, which work together to provide reliable data that is used for path planning and localization.
Some of the notable features are:
- AGV is capable of marking field lines on any sports field
- Uses GPS, IMU, and encoder sensors for input from the robot for state estimation and motion planning
- Sensors are fused to provide reliable data for path planning and localization of the robot
- The system was implemented in Matlab-Simulink and tested first and then the prototype was built and run on the field using ROS melodic in Raspberry Pi.
- The bot was capable of 4-wheel steering and drive making it capable of navigating over any terrain with ease and not comprising accuracy.
Machinehole Scavenger
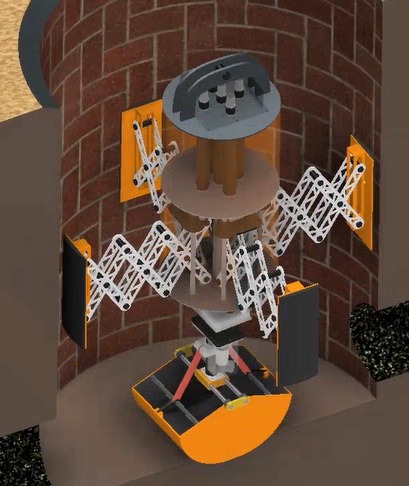 MachineHole-Scavenger is an innovative mechatronic system designed to efficiently clean manhole sewage waste using advanced sensors and actuators. The project aims to eliminate the risks associated with manual scavenging by implementing a robotic solution. With a combination of encoders, moisture sensors, and gas sensors, the system can monitor the environment and the robot itself, providing a high degree of flexibility. Users can control the complex mechatronic system easily through a simple button and joystick configuration, thanks to kinematics and dynamic modeling. The mechanical aspects involve synchronized mechanisms, such as an independent jack for X and Y motion, a leadscrew-powered prismatic joint for z-axis actuation, and a separate actuator for rotation. The MachineHole-Scavenger's design ensures efficient and effective cleaning of manhole sewage waste.
MachineHole-Scavenger is an innovative mechatronic system designed to efficiently clean manhole sewage waste using advanced sensors and actuators. The project aims to eliminate the risks associated with manual scavenging by implementing a robotic solution. With a combination of encoders, moisture sensors, and gas sensors, the system can monitor the environment and the robot itself, providing a high degree of flexibility. Users can control the complex mechatronic system easily through a simple button and joystick configuration, thanks to kinematics and dynamic modeling. The mechanical aspects involve synchronized mechanisms, such as an independent jack for X and Y motion, a leadscrew-powered prismatic joint for z-axis actuation, and a separate actuator for rotation. The MachineHole-Scavenger's design ensures efficient and effective cleaning of manhole sewage waste.
Intelligent Picking - Flipkart Grid 2.0
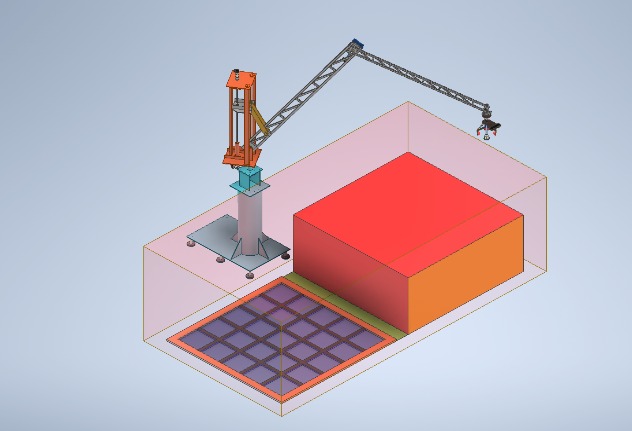 The project is based on automating the process of picking and placing objects in the manufacturing and warehouse industry. It involves the use of a camera, an articulated arm, and optimized algorithms to pick heavy payloads accurately and efficiently. The system employs path-planning techniques to navigate the arm to the desired location while taking into account obstacles in its way.
The project is based on automating the process of picking and placing objects in the manufacturing and warehouse industry. It involves the use of a camera, an articulated arm, and optimized algorithms to pick heavy payloads accurately and efficiently. The system employs path-planning techniques to navigate the arm to the desired location while taking into account obstacles in its way.
- Intelligent picking system using an onboard camera
- Articulated arm with optimized design to pick heavy payloads
- Path planning to achieve accurate and efficient movement
- Kinematics involved in the arm movement
- PID control for precise control and stability while picking and placing objects
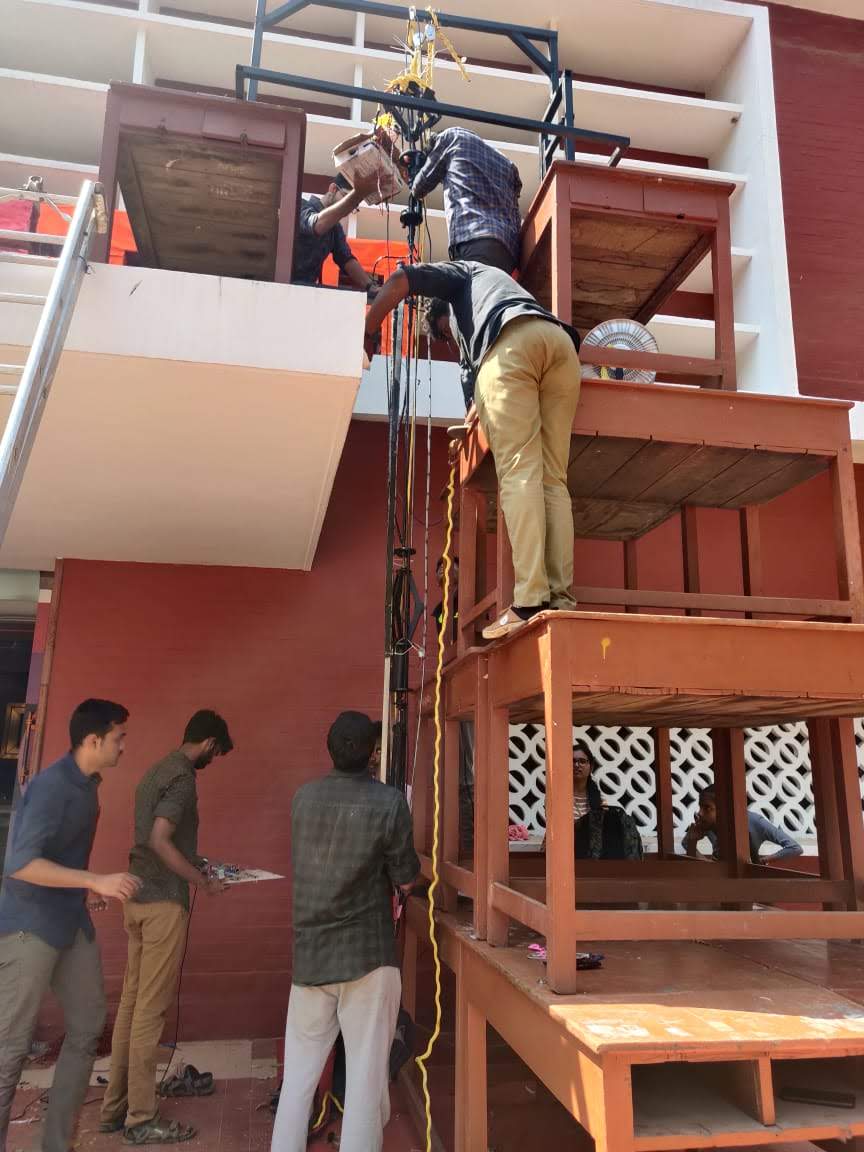

Borewell Rescue Bot
 An innovative solution was developed to address the pressing issue of animals and infants getting trapped in deep holes. The rescue bot was designed and coded with a control system to ensure the successful retrieval of these victims. The bot was designed with various features that allow it to navigate through difficult terrains, reach the victims, and safely lift them to the surface. The control system of the bot was developed by integrating various sensors, actuators, and algorithms that allowed it to make real-time decisions and execute precise movements.
An innovative solution was developed to address the pressing issue of animals and infants getting trapped in deep holes. The rescue bot was designed and coded with a control system to ensure the successful retrieval of these victims. The bot was designed with various features that allow it to navigate through difficult terrains, reach the victims, and safely lift them to the surface. The control system of the bot was developed by integrating various sensors, actuators, and algorithms that allowed it to make real-time decisions and execute precise movements.
- Wireless RF connection between the controller and the bot
- Use of 5 DOF Parallel Manipulator used to maximize the reach of the limited workspace
- Real-time feedback on the environment using various sensors
- Real-time feedback on the bot pose
Personal Projects
Animetronic Hand
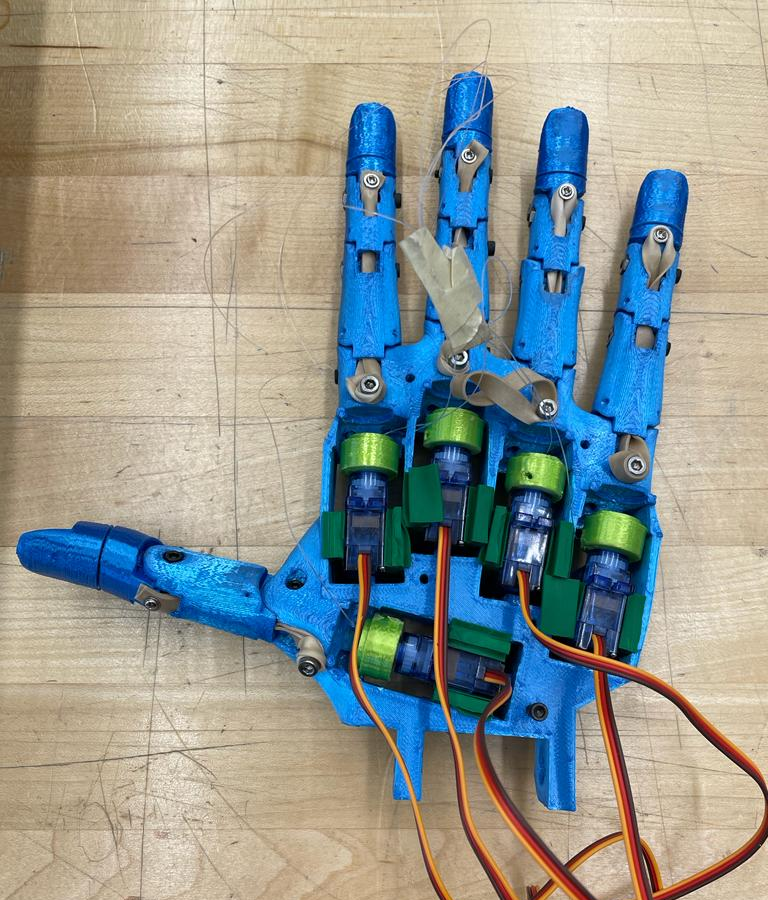 The Animetronic-Hand project aimed to develop a gesture-controlled animetronic hand for teleoperation, focusing on enhancing accessibility for differently-abled individuals. It was created as a proof of concept during the "Byte into Hardware" Hardware Hackathon at NJIT. The project utilized computer vision techniques for gesture tracking and interpretation, allowing users to control the hand's movements. Hardware components included a 3D printed animetronic hand, Tower Pro Servos, a Logitech webcam, Arduino, and an IMU. The hand's 3D model was split and printed on multiple printers due to its long print duration. Gesture tracking and control relied on the Mediapipe package to locate and calibrate keypoints, enabling accurate actuation commands for the animetronic hand. The project's architecture successfully integrated computer vision, hardware components, and calibration techniques to create an interactive and accessible system.
The Animetronic-Hand project aimed to develop a gesture-controlled animetronic hand for teleoperation, focusing on enhancing accessibility for differently-abled individuals. It was created as a proof of concept during the "Byte into Hardware" Hardware Hackathon at NJIT. The project utilized computer vision techniques for gesture tracking and interpretation, allowing users to control the hand's movements. Hardware components included a 3D printed animetronic hand, Tower Pro Servos, a Logitech webcam, Arduino, and an IMU. The hand's 3D model was split and printed on multiple printers due to its long print duration. Gesture tracking and control relied on the Mediapipe package to locate and calibrate keypoints, enabling accurate actuation commands for the animetronic hand. The project's architecture successfully integrated computer vision, hardware components, and calibration techniques to create an interactive and accessible system.
Smart Bin
The Smart-Bin project focuses on developing an intelligent dustbin capable of sorting waste into four categories: Domestic, Metal, Plastic, and Glass. The system utilizes an ESP32 microcontroller and a camera module to capture images of the trash deposited by the user. These images are then sent to a central computer, which runs a machine learning model designed to classify the waste into the appropriate category. The output from the model determines the bin in which the waste should be placed.
To ensure reliable classification, the Smart-Bin project incorporates proper lighting conditions to optimize image quality and enhance the accuracy of the waste sorting process. By combining the capabilities of the ESP32 microcontroller, camera module, and machine learning model, the Smart-Bin aims to automate waste sorting and promote efficient recycling practices.
Single Point Self Balanced guided vehicle powered by Gyroscope with high maneuverability.
It is an innovative object that is designed to provide a high degree of maneuverability, stability, and safety. It is equipped with sensors and control systems that help it maintain its balance and stability, even in the face of changing conditions. The self-balanced guided vehicle powered by a drone gives a high degree of accurate control on the plane assisted with a rotating disc giving gyroscopic stability.